Alan, Ben, Calvin and Dean shared some postcards. Alan received 20% of the postcards. Ben received 16 fewer postcards than Alan. Calvin received twice as many postcards as Ben. Dean got the remaining 144 postcards.
(a) find the total number of postcards shared by Alan, Ben, Calvin and Dean
(b) how many per cent more postcards than Alan did Dean receive?
Showing posts with label 2 Model Approach To Problem Solving. Show all posts
Showing posts with label 2 Model Approach To Problem Solving. Show all posts
Tuesday, May 4
Tuesday, April 13
Utilising Advancd UTM Techniques
Mrs Lim said...
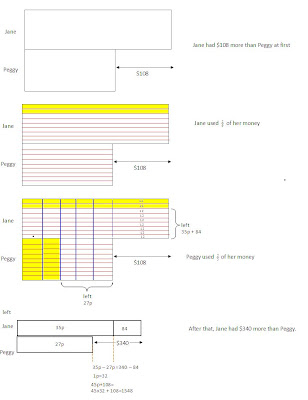
- I have bought your Unit Transfer Method Book last month. I was trying to use Chapter 1.4 (All Changing Quanties) to solve the below question from my girl's P6 test paper but somehow just could not solve the question. Question: Jane had $108 more than Peggy at first. Jane used 2/9 of her money while Peggy used 2/5 of her money. After that, Jane had $340 more than Peggy. How many did Jane have at first?
- April 11, 2010 9:16 AM
Problems that involve “more than/less than” generally utilize Advanced UTM technique. This problem cannot be solved using “All changing quantities” – questions in “All changing” does not involve “more than/ less than”.
I would advise to teach the child the basic UTM technique and ensure the child is proficient in applying the fundamental UTM framework before to expose them to the advanced UTM. Without the basic training in the UTM framework, the child will faces challenges in visualizing the above conversion and may end up confusing the child.
Below depicts an alternate method to the above problem using the stack model approach :
Tuesday, March 16
The Maths Challenge to Parent - UTM book Q5 Pg 20
Hi Sunny
My daughter was trying out the Q5 on page 20 of your UTM book. I have download the answers and explanation, but I don't seem to understand what the "40" in the boxes that you have placed in the diagram. How did you derive the "40"?
My daughter was trying out the Q5 on page 20 of your UTM book. I have download the answers and explanation, but I don't seem to understand what the "40" in the boxes that you have placed in the diagram. How did you derive the "40"?
Question: Three sisters, Angie, Bernice and Candice share some sweets. Angie's share is 40% of the total number of sweets the three sisters have. Bernice has 40 sweets more than Angie. Bernice's share is 4 times Candice’s. How much money did each of them have?
Thanks
Vijay
Thanks
Vijay
From the Desk of Sunny Tan........
Thursday, February 25
Saturday, February 20
Maths Problem
Hi Sunny,
From the Desk of Sunny Tan........
(click on image for larger view)

Greetings!
My daughter, have attended your PR. 6 sesson.
I have one of her Pr. 6 problem that I know the answer but do not know how to present to her. Based on your method, how do you solve the following question:
Ai Tong School organized a 2-day camp. On the first day, the number of boys was 600 more than the girls. On the second day, the number of boys decreased by 10% but the number of girls increased by 10%. If there were 2540 children on the second day, how many children were there on the first day?Appreciate your enlightening on the solution.
Thanks.
Mr LeeFrom the Desk of Sunny Tan........
(click on image for larger view)

Friday, March 6
Unit Transfer Method Versus Model Drawing
The question is the excerpt from the UTM publication, Chapter 1.1.
The following question is used to illustrate the Model Approach and Unit Transfer Method.
You will realise that the fundamental concept between UTM and MD is the same. While MD uses bar diagram and visual spatialisation, UTM uses tabulation and logical reasoning.
Question
5/6 of the buses were owned by Company C and the rest by Company S. Company S bought another 900 buses and now owns 2/3 of all the buses. How many buses does Company S have now?
Answer:

Try to solve the following using UTM:
Tom had a box of red beads and yellow beads. When he added in 30 red beads, 20% of the beads were yellow beads. He added another 100 yellow beads; as a result, 60% of the beads in the box were yellow. How many red beads were there in the box at first?
The following question is used to illustrate the Model Approach and Unit Transfer Method.
You will realise that the fundamental concept between UTM and MD is the same. While MD uses bar diagram and visual spatialisation, UTM uses tabulation and logical reasoning.
Question
5/6 of the buses were owned by Company C and the rest by Company S. Company S bought another 900 buses and now owns 2/3 of all the buses. How many buses does Company S have now?
Answer:

Try to solve the following using UTM:
Tom had a box of red beads and yellow beads. When he added in 30 red beads, 20% of the beads were yellow beads. He added another 100 yellow beads; as a result, 60% of the beads in the box were yellow. How many red beads were there in the box at first?
Thursday, February 26
Parents' Concern
Hi Sunny
Please elaborate more on UTM.
Is it a more effective method as compared to other Heuristics?
Is model drawing or Guess and Check a waste of time?
Will the child be confused if he/she is taught a different method from schools?
Concerned parents
Hi Sunny,
Good Afternoon Sir,
As the name of your blog suggests, there is no better way to learn more about UTM than from the guru himself.
As compared to Model Drawing, UTM lacks the visual impact which enables a student to see Maths,so to speak.
In what way is UTM a more effective method than MD?
Could you help to illustrate with some examples?
Is UTM within MOE Maths syllabus?
Interested parents
From the desk of Sunny Tan ... ...
UTM RESEARCH BACKGROUD
The Unit Transfer Method is a fundamentally sound approach with research based on Teacher Work Series publication. Unit Transfer Method uses ratio with tabulation to help child to effectively analyze and solve challenging mathematical problems. This simple, logical yet powerful problem-solving technique is an alternative to the model approach and the algebraic framework approach.
MOE SYLLABUS
Reference to MOE forum replies “Different Approaches taught for Mathematical Techniques” dated 12th Feb 2007, Ms Ho Peng, Director, Curriculum Planning and Development.
“Other than the model drawing approach, pupils are also taught different problem solving methods. They are encouraged to try different approaches and have the flexibility to choose the method that works best for them in solving the problems’
“In the marking of PSLE mathematics, pupils are not restricted to the use of any one particular method. All mathematically correct solutions are acceptable”
In the replies above, the Ministry of Education will accept any mathematically correct method in the PSLE. In fact, the reply mentioned that pupils need a wider repertoire of approaches to work with more challenging problems.
The UTM is very effective in solving problems involving the Before and After Concept, which is one of the heuristics stipulated in the MOE curriculum.
PROBLEM SOLVING HEURISTICS
MOE has recommended 11 problem solving heuristics in primary level. Every heuristics plays a role in problem solving. The common misconception in many parents is that many are trying to search for the “holy Grail” or the most “superior” problem solving methods for their child.
Many parents have always raised these concerns during my seminar, “Is guess and check or model drawing a waste of time?” To answer these concerns, we have to ask ourselves "What is heuristics?"
Heuristics are methods that helps in problem solving. Heuristics does not guarantee a solution.
When approaching the problem, the child first understands the problem, chooses the method and carry out the plan. If it doesn’t work, the method should be discarded and a new method should be choose to solve the problem. However, many pupils or even us will “stubbornly” continue to usie the initial method even it doesn’t work!
UTM VERSUS MODEL APPROACH
As mentioned, many parents are guilty of searching for the “Holy Grail” or the most “Superior” problem solving method. We all know in fact, they never or will never exist.
Different children have different learning style - right and left brain dominant learners.
The left brain learners are strong in logical and analytical thinking while the right brain learner seeks to determine the spatial/visual relationships of all the parts.
The question of which is more superior method is therefore very subjective. Therefore, we cannot answer on behalf of our child. What is important as parents, we should equip the child with different approaches so that they have the flexibility to choose the method that works best for them in solving the problems.
The fundamental concept of the model approach and UTM utilizes ratio. Model drawing is visual or UTM uses tabulation. The combination of Model Approach and Unit Transfer Method utilize the left and the right brain- an integrated "whole" brain approach to maximize the untapped potential of the child.
VISUAL PROCESSING TECHNIQUE
“Do you know Guess and Check can be solved just by using 3 steps?”
“Do you know there are other ways to draw model other than horizontal bar?
By changing the orientation of the model, the answers is staring in front of them!
These are some of the topics that will be covered in the Parents’ Seminar.
Please elaborate more on UTM.
Is it a more effective method as compared to other Heuristics?
Is model drawing or Guess and Check a waste of time?
Will the child be confused if he/she is taught a different method from schools?
Concerned parents
Hi Sunny,
Good Afternoon Sir,
As the name of your blog suggests, there is no better way to learn more about UTM than from the guru himself.
As compared to Model Drawing, UTM lacks the visual impact which enables a student to see Maths,so to speak.
In what way is UTM a more effective method than MD?
Could you help to illustrate with some examples?
Is UTM within MOE Maths syllabus?
Interested parents
From the desk of Sunny Tan ... ...
UTM RESEARCH BACKGROUD
The Unit Transfer Method is a fundamentally sound approach with research based on Teacher Work Series publication. Unit Transfer Method uses ratio with tabulation to help child to effectively analyze and solve challenging mathematical problems. This simple, logical yet powerful problem-solving technique is an alternative to the model approach and the algebraic framework approach.
MOE SYLLABUS
Reference to MOE forum replies “Different Approaches taught for Mathematical Techniques” dated 12th Feb 2007, Ms Ho Peng, Director, Curriculum Planning and Development.
“Other than the model drawing approach, pupils are also taught different problem solving methods. They are encouraged to try different approaches and have the flexibility to choose the method that works best for them in solving the problems’
“In the marking of PSLE mathematics, pupils are not restricted to the use of any one particular method. All mathematically correct solutions are acceptable”
In the replies above, the Ministry of Education will accept any mathematically correct method in the PSLE. In fact, the reply mentioned that pupils need a wider repertoire of approaches to work with more challenging problems.
The UTM is very effective in solving problems involving the Before and After Concept, which is one of the heuristics stipulated in the MOE curriculum.
PROBLEM SOLVING HEURISTICS
MOE has recommended 11 problem solving heuristics in primary level. Every heuristics plays a role in problem solving. The common misconception in many parents is that many are trying to search for the “holy Grail” or the most “superior” problem solving methods for their child.
Many parents have always raised these concerns during my seminar, “Is guess and check or model drawing a waste of time?” To answer these concerns, we have to ask ourselves "What is heuristics?"
Heuristics are methods that helps in problem solving. Heuristics does not guarantee a solution.
When approaching the problem, the child first understands the problem, chooses the method and carry out the plan. If it doesn’t work, the method should be discarded and a new method should be choose to solve the problem. However, many pupils or even us will “stubbornly” continue to usie the initial method even it doesn’t work!
UTM VERSUS MODEL APPROACH
As mentioned, many parents are guilty of searching for the “Holy Grail” or the most “Superior” problem solving method. We all know in fact, they never or will never exist.
Different children have different learning style - right and left brain dominant learners.
The left brain learners are strong in logical and analytical thinking while the right brain learner seeks to determine the spatial/visual relationships of all the parts.
The question of which is more superior method is therefore very subjective. Therefore, we cannot answer on behalf of our child. What is important as parents, we should equip the child with different approaches so that they have the flexibility to choose the method that works best for them in solving the problems.
The fundamental concept of the model approach and UTM utilizes ratio. Model drawing is visual or UTM uses tabulation. The combination of Model Approach and Unit Transfer Method utilize the left and the right brain- an integrated "whole" brain approach to maximize the untapped potential of the child.
VISUAL PROCESSING TECHNIQUE
“Do you know Guess and Check can be solved just by using 3 steps?”
“Do you know there are other ways to draw model other than horizontal bar?
By changing the orientation of the model, the answers is staring in front of them!
These are some of the topics that will be covered in the Parents’ Seminar.
Wednesday, August 6
2 questions - Mrs Tan
Hi Sunny,
Please advise how to solve the following using UTM:
1. Ryan and Jude have some pencils each. If Ryan give Jude 28 pencils, he will have as many pencils as Jude. If Ryan gives Jude 12 pencils, he will have many pencils as Jude. How many pencils does each of them have?
2. At a party, Mrs. Lim serves either lemonade in glasses or cups. She has exactly 100 glasses or 150 cups of lemonade. If she has already served her guests 40 glasses and 28 cups of lemonade, what is the maximum number of glasses of lemonade she had left?
Question posted by Mrs Tan, Parent
Fri, 5th Dec 2008
From the desk of Sunny Tan ... ...
click on picture for bigger view


Please advise how to solve the following using UTM:
1. Ryan and Jude have some pencils each. If Ryan give Jude 28 pencils, he will have as many pencils as Jude. If Ryan gives Jude 12 pencils, he will have many pencils as Jude. How many pencils does each of them have?
2. At a party, Mrs. Lim serves either lemonade in glasses or cups. She has exactly 100 glasses or 150 cups of lemonade. If she has already served her guests 40 glasses and 28 cups of lemonade, what is the maximum number of glasses of lemonade she had left?
Question posted by Mrs Tan, Parent
Fri, 5th Dec 2008
From the desk of Sunny Tan ... ...
click on picture for bigger view


Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)